
Jigsaw Learning
How does an everyday object work?
Jigsaw Learning Interactive Video Guided Discovery
Team: Qianhui Sun, Mingtong Zhang
My Role: Video Editing & Instructional Design
Duration: 2 weeks
01
WHAT JIGSAW LEARNING IS
Definition:
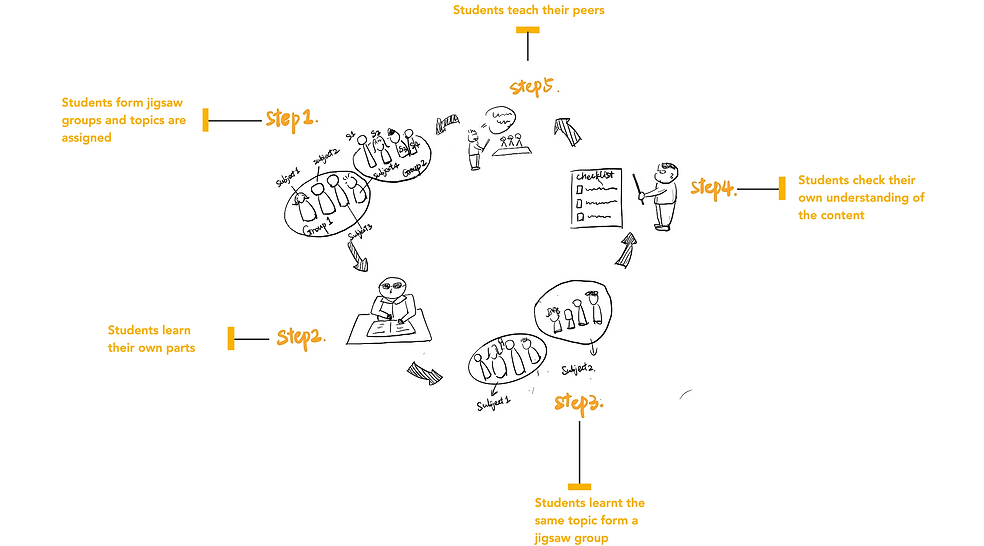
Jigsaw is a group learning activity in which each student must cooperate with peers to achieve learning goals. Students form a jigsaw group. Teachers assign different topics to different students in the group. Students need to learn and become an expert in their own topics first. Then, they teach their part to other teammates. The final assessment for everyone will cover all the topics, including yours and your teammate's ——just like a jigsaw puzzle —there is no single piece that could be missed in order to assemble the whole picture of learning.
Background:
Jigsaw learning originated in 1970s when racial discrimination is a serious problem in the classroom. A genius social psychologist Elliot Aronson created this approach to let students rely on each other to succeed. In this way, they learn to set aside racial issues.
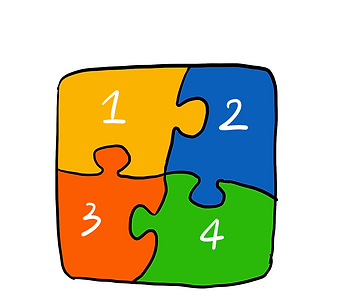
Each student is assigned a topic
02
FINAL DEMO

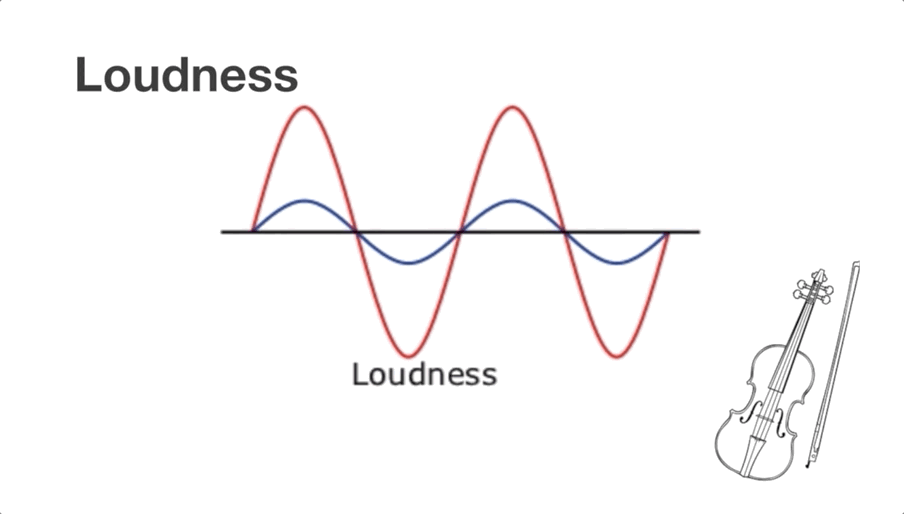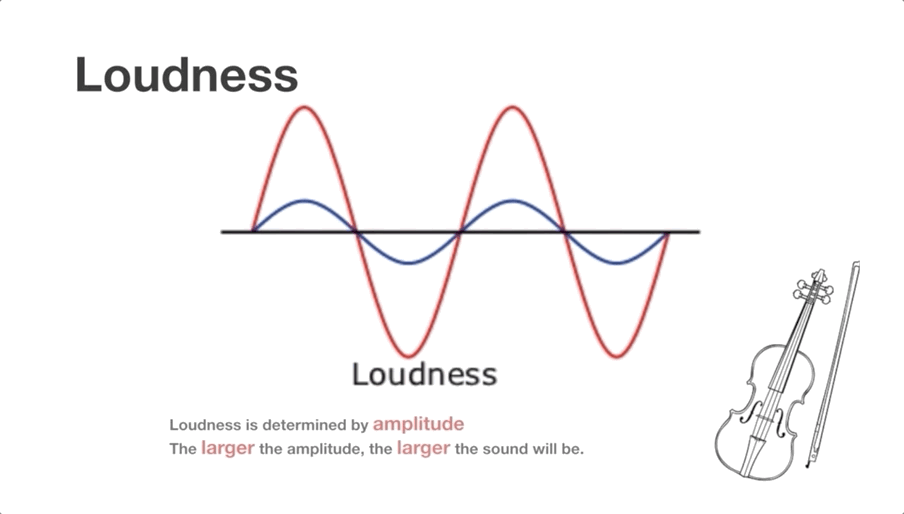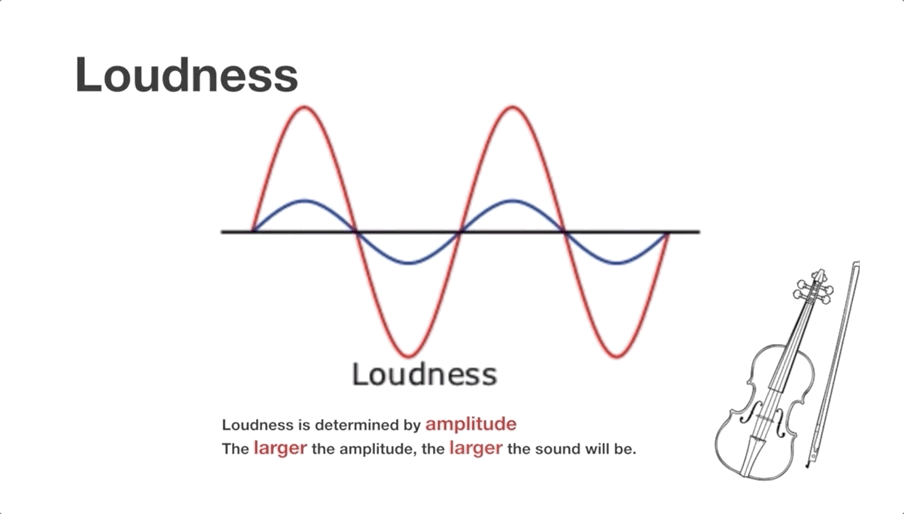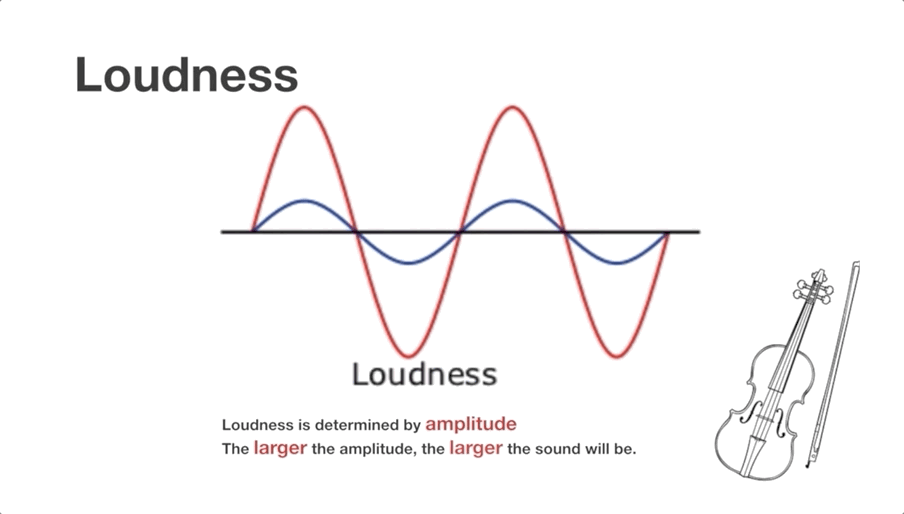
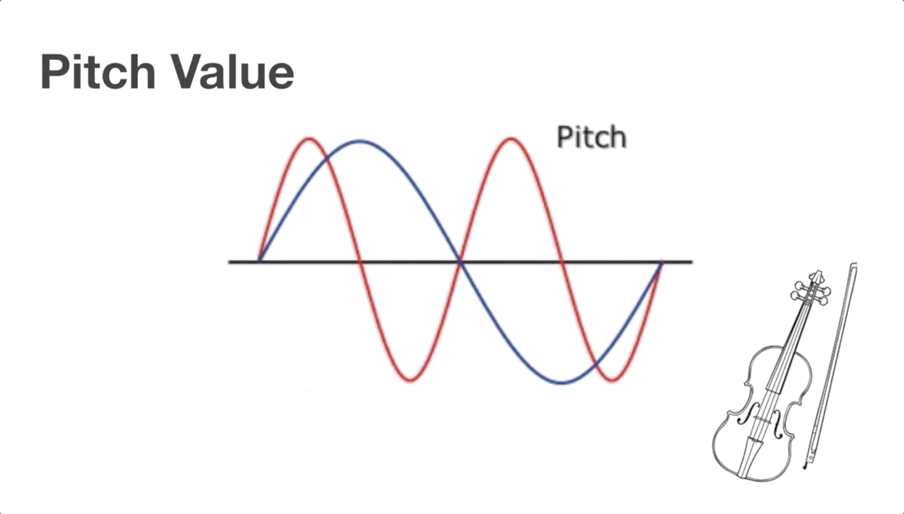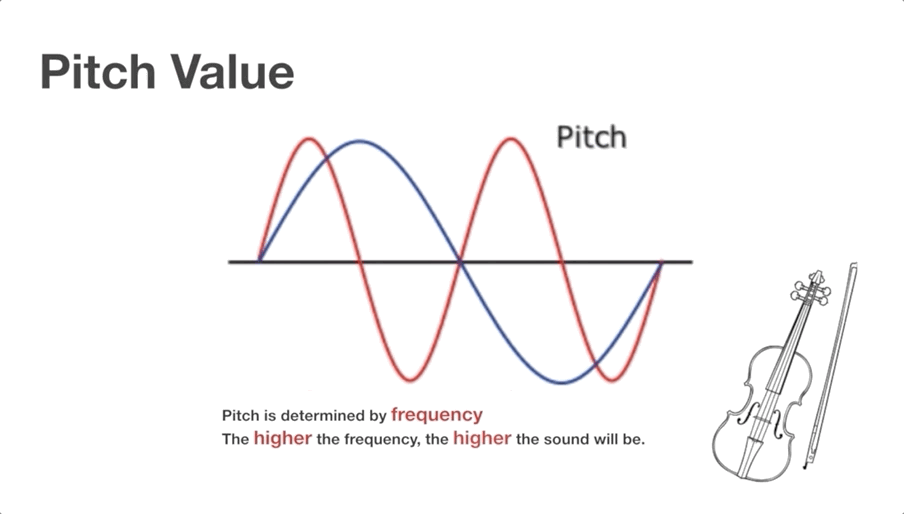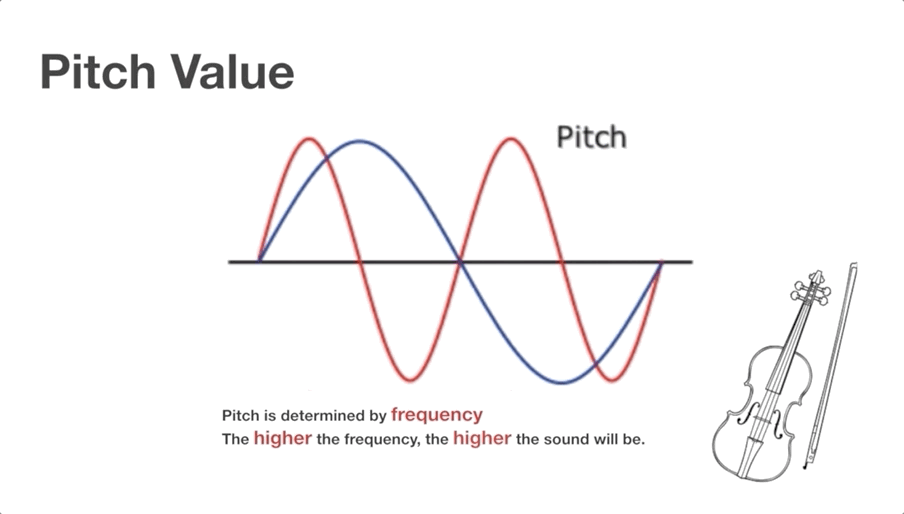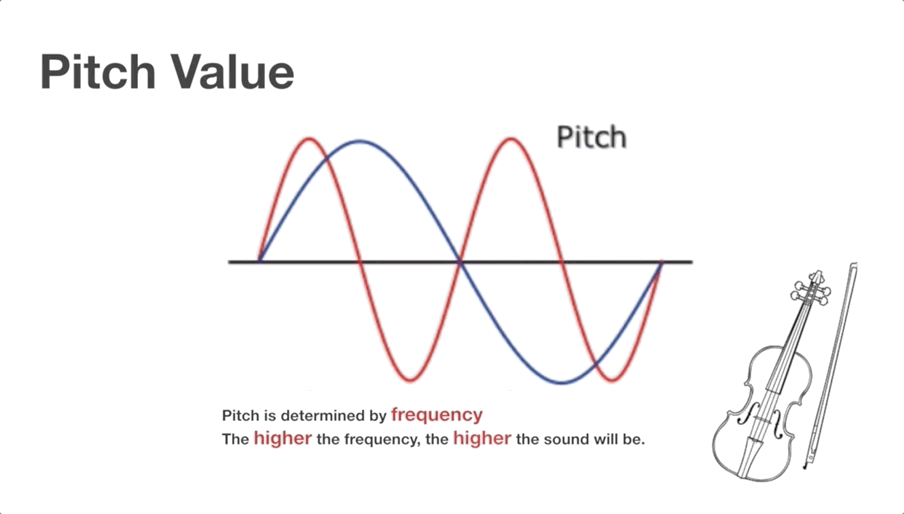
Video Clip 1 (shared by all learners):
-
The structure of violins and the mechanism of generating sounds
After Video Clip 1, learners will be asked to choose a topic they want to learn.
Video Clip 2:
-
Topic 1: Sound loudness
Video Clip 3:
-
Topic 2: Sound pitch




What are the steps in a jigsaw video?
1. Watch an Introductory video
When learners log onto our platform, there would be an introductory part telling them what jigsaw learning is.
2. Choose / Be assigned a Topic
Learners would be asked to choose a topic to learn. Once a topic is chosen by one learner, others will not be able to choose it again. Teachers could also assign a topic to student in an asynchronous learning setting.
3. Watch your Video Clip
Learners will watch a video clip under their chosen topic.
4. Do a Mastery Check
After watching the video, they need to answer several questions to check their understanding. Ideally, in a face-to-face classroom, learners under the same topic could form an expert group to discuss together.
5. Teach with a Checklist in Mind
A checklist appears on screen as a self-check & self-reminder of the knowledge components need to be covered when teaching other group members.
6. Do an Overall Summative Test
Finally, learners need to take a summative test that covers all the topics. Final score would be a weighted average of everyone's score.
03
HOW JIGSAW LEARNING WORKS
-
What are the steps in a typical jigsaw learning loop?
-
What are the benefits of jigsaw learning?
-
What are the challenges and potential pitfalls of jigsaw learning?
Benefits:
-
Teach empathy & Increase group cohesion
-
Increase classroom efficiency
-
Close achievement gaps
Key Elements:
-
Shared learning goals
-
Positive interdependence between students
-
Teachers clear misconceptions
04
DESIGN JUSTIFICATION
1. Motivation
The motivation of learners include positive interdependence and individual accountability. We anticipated that learners would follow the instructional sequence that we designed.
2. Hypothesized Cooperation
Learners have shared learning goals, which is to understand how the violin works. They also want to score as high as possible in the final test.
3. Design of Cooperative Scaffold
The only way that learners could learn all the content is through their partners, which fosters positive interdependence. We created formative tests to check the learner's understanding of their parts first before teaching their peers. We also provided elaborative feedback to correct learners' misunderstandings.
For individual accountability, as both learners take the same quiz and their score is averaged, helping other learners learn is to the maximum of their own interests as well.
05
FINAL THOUGHTS
The most important element in a jigsaw learning group is positive interdependence. In an online setting which students don't get the chance to meet each other, it is especially important to build positive interdependence through mechanism like weighted grading.
